Mingjie Pu, Wanlin Guo, Yufeng Guo
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces , 15, 50, 58388-58396, 2023.
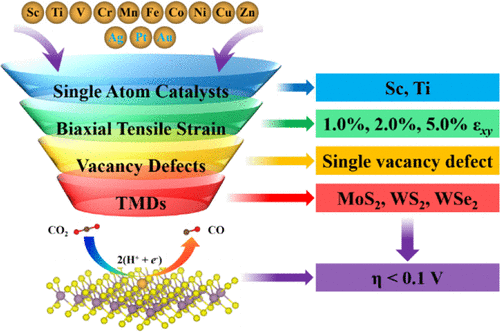
Abstract: Using non-noble metal atoms as catalysts is attractive for decreasing the cost of the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). By screening first-row transition metals and noble metals through extensive first-principles calculations, non-noble Sc and Ti single atoms binding on vacancy-defected transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) monolayers exhibit better catalytic performance and selectivity for electrochemical CO2RR than noble metal single atoms. The overpotentials of Sc and Ti atoms for the CO2RR can be reduced lower than 0.09 V after applying suitable biaxial tensile strains on vacancy-defected TMDs, which are approximately 1 order of magnitude lower than that of most reported metal atom catalysts. The vacancy defects of TMDs and charge transfer to metal atoms induced by tensile strain play a key role in improving the catalytic activity of non-noble metal single atoms. These results highlight a possible way to design new single atom catalysts for electrochemical CO2RR by utilizing the combination of non-noble metal atoms, defected TMDs, and strain engineering.
Keywords: CO2 reduction reaction; metal single atom catalysts; vacancy; transition metal dichalcogenides; strain engineering
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsami.3c13240