Jiafen Cao, Mengqi Gu, Wanlin Guo
International Journal of Fatigue ,2025,109430
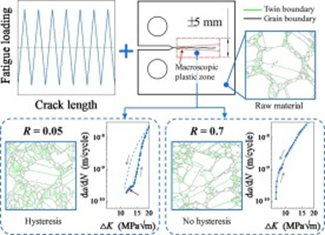
Abstract: It is widely recognized that the near-threshold slow fatigue crack growth (FCG) in metals is sensitive to their microstructures and the damage zone well within the crack tip plastic zone is the root form FCG. Here we find that near-threshold slow FCG can induce evolution of cyclic microplastic deformation which can significantly change the microstructures in a much larger region than the macroscopic crack tip plastic zone evaluated by classic continuum fracture mechanics theory in compact tension specimens of a Ni-based superalloy at both low and high stress ratios under ambient conditions. Detailed analyses utilizing electron backscatter diffraction and scanning electron microscopy examination reveal that, at low stress ratio of 0.05, near-threshold FCG induces evolution in microstructures through twinning and exhibited hysteresis. While microstructure evolution at high stress ratio of 0.7 is dominated by lattice torsion resulting from dislocation pile-up, without hysteresis. This shows that irreversible cyclic microplastic deformation can induce microstructure changes far outside the macroscopic crack tip plastic zone where the cyclic stress is far below the yield strength of material. The results fundamentally challenge the conventional conception that damage accumulation only occurs within the macroscopic plastic zone, deepen our understanding of why fatigue can occur well below the traditional fatigue limit and FCG continues below the “threshold value”, guiding our design for long life structures.
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142112325006279